ProvNeRF: Modeling per Point Provenance in NeRFs as a Stochastic Field
Kiyohiro Nakayama1 Mikaela Angelina Uy1, 3 Yang You1 Ke Li2 Leonidas J. Guibas1
1Stanford University
2Simon Fraser University
3NVIDIA
2024 Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2024)
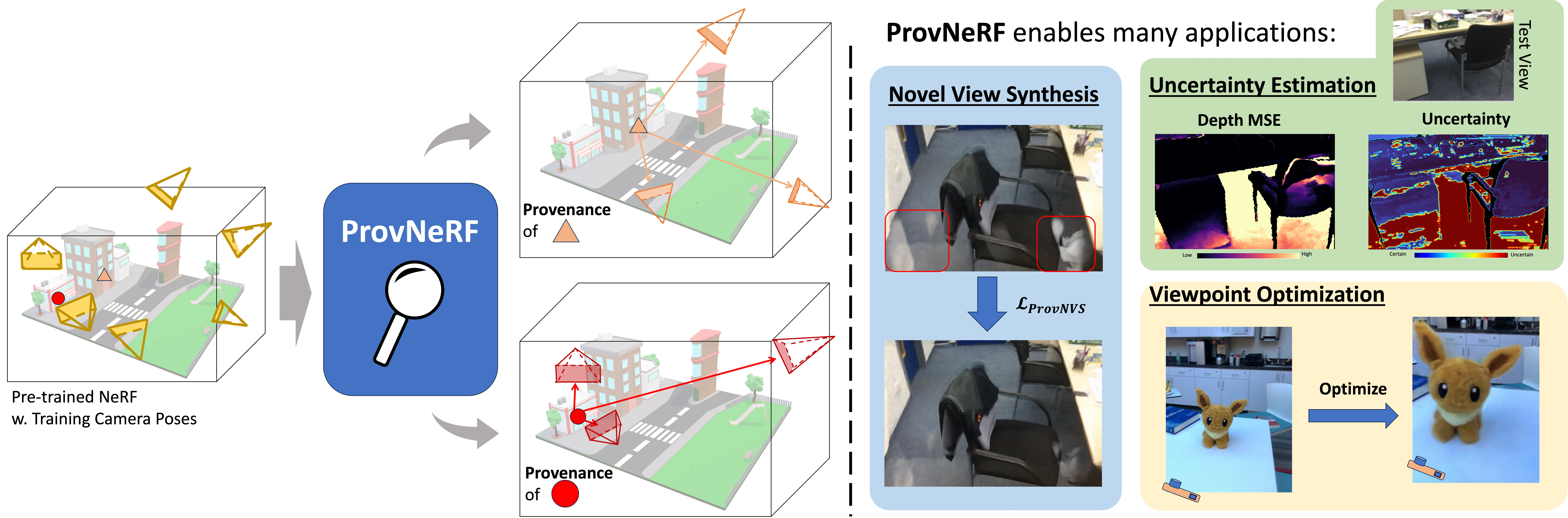
(Left) ProvNeRF models a provenance field that outputs provenances for each 3D point as likely samples (arrows).
For 3D points (brown triangle and blue circle), the corresponding provenances (illustrated by the arrows), are locations that likely observe them.
(Right) ProvNeRF enables better novel view synthesis and estimating the uncertainty of the capturing process
because it models the locations of likely observations that is critical for NeRF's optimization.
Method Overview
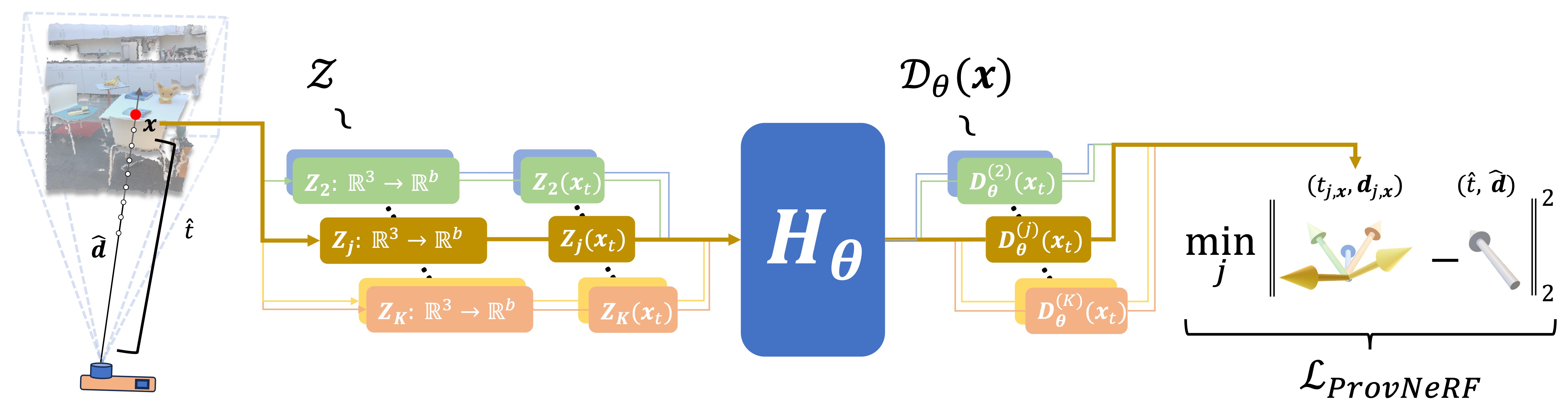
Training pipeline for ProvNeRF For each point x seen from provenance,
with direction d at distance t, we first sample K latent random functions from distribution.
The learned transformation H transforms each latent function sample to a provenance sample.
Supplementary Video
Application 1: Uncertainty Modeling
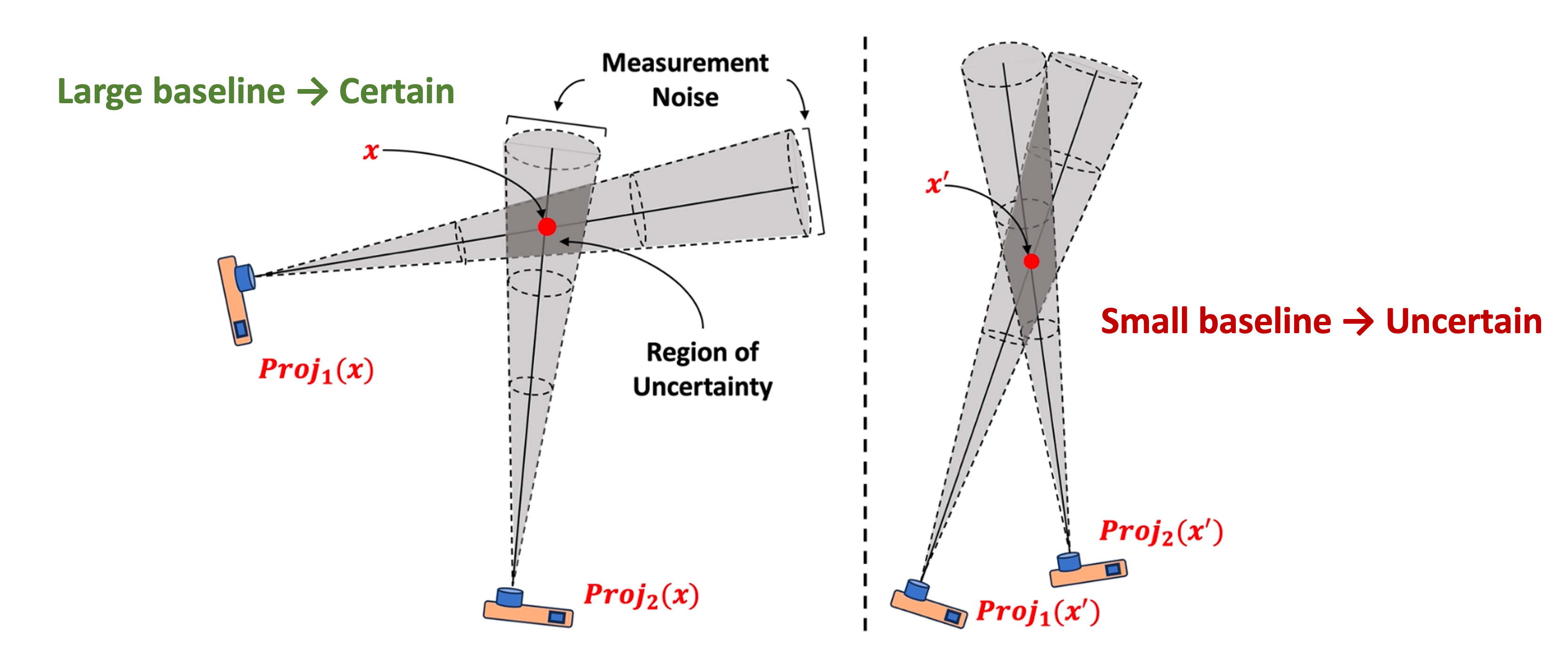
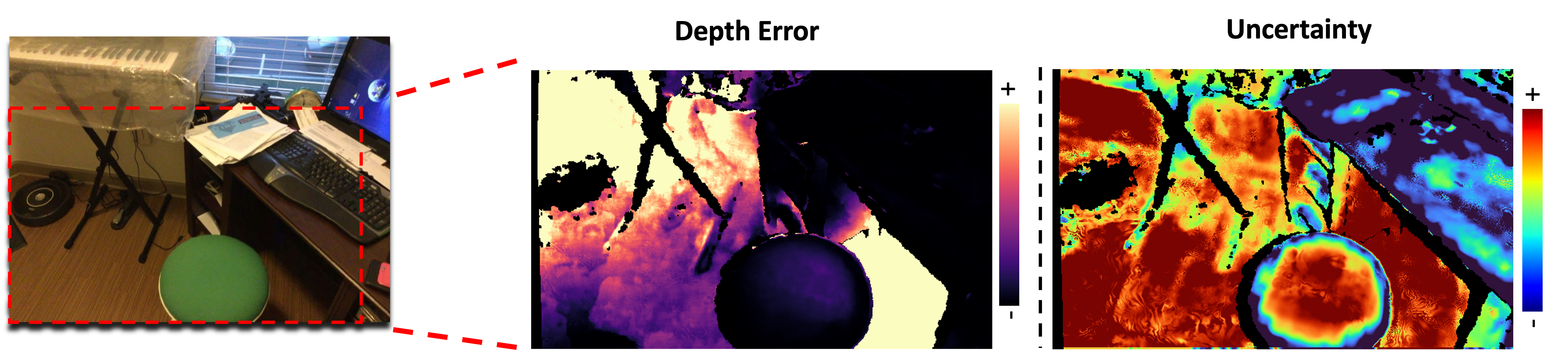
Uncertainty of the capturing process strongly depends on the angles between observations.
For example, a larger camera baseline would lead to small regions of uncertainty.
a small baseline leads to large uncertainty region.
We leverage literature on multi-view geometry to quantify this intuition as the posterior probability of each point given the provenance predictions.
Scannet 710
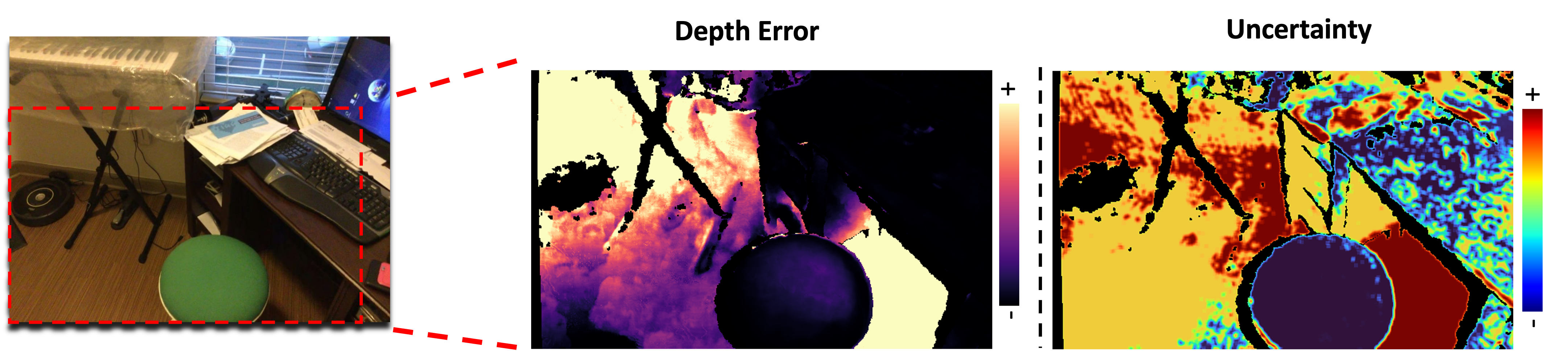
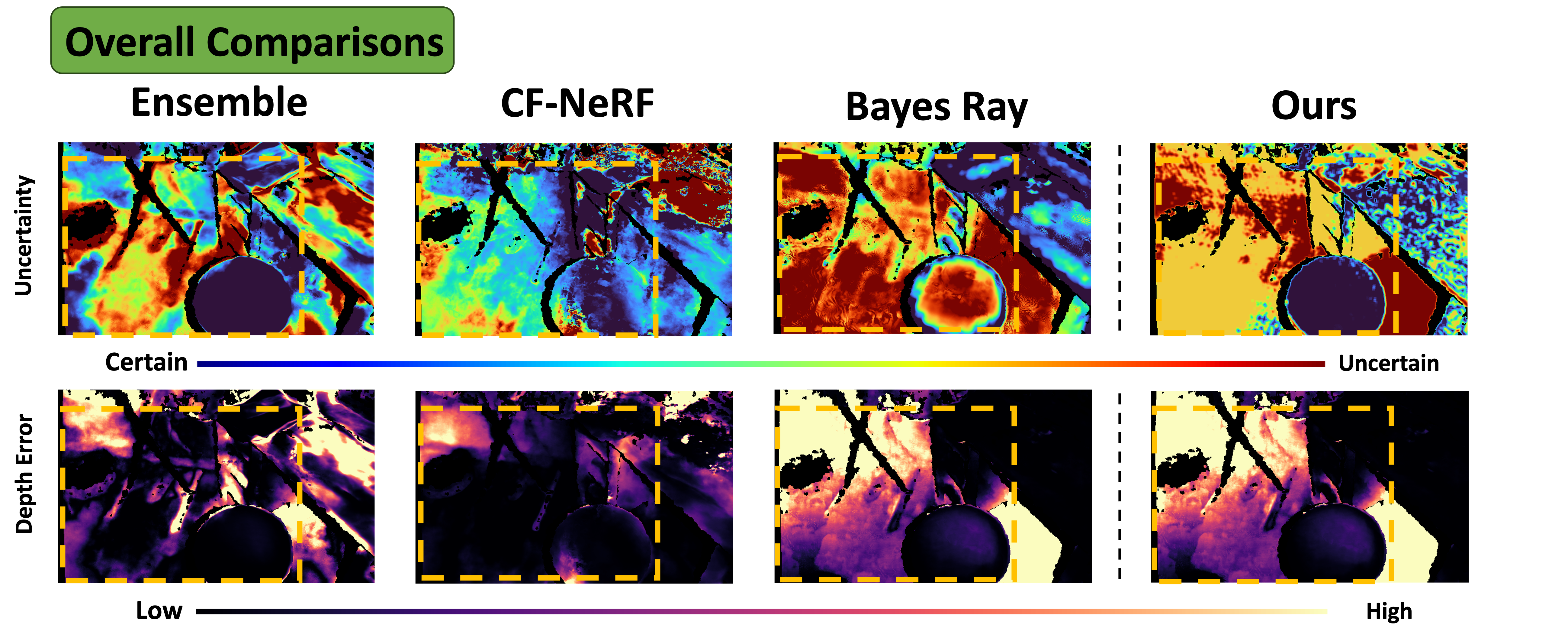
Scannet 758
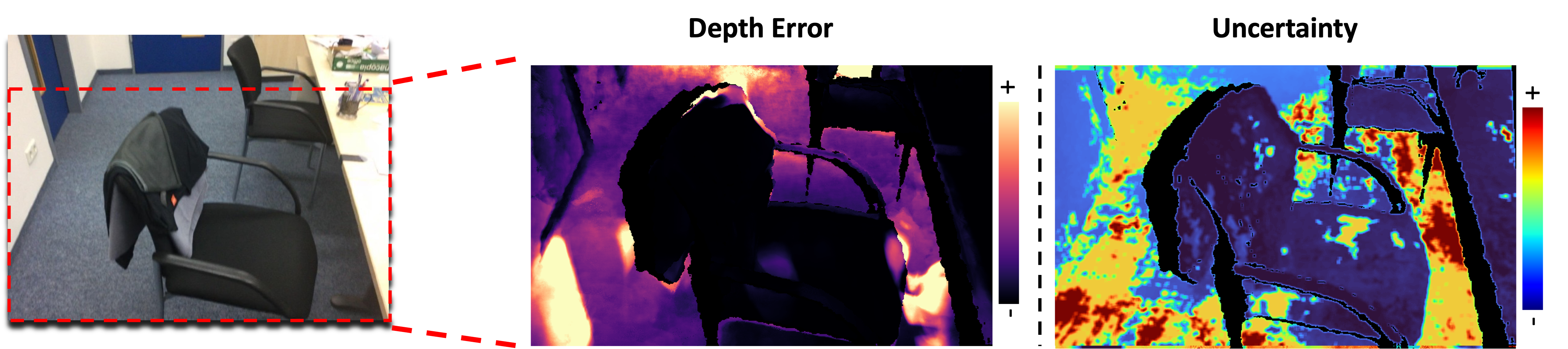
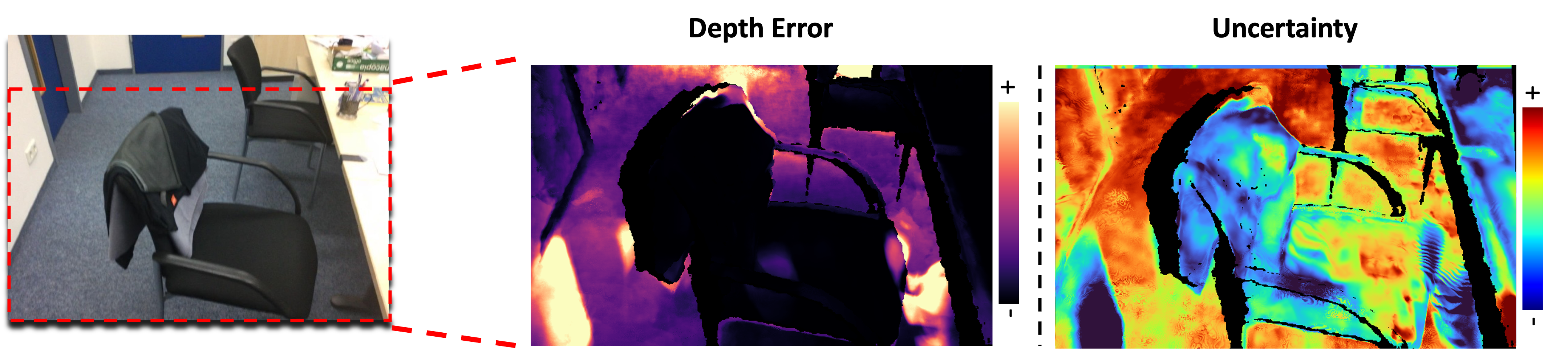


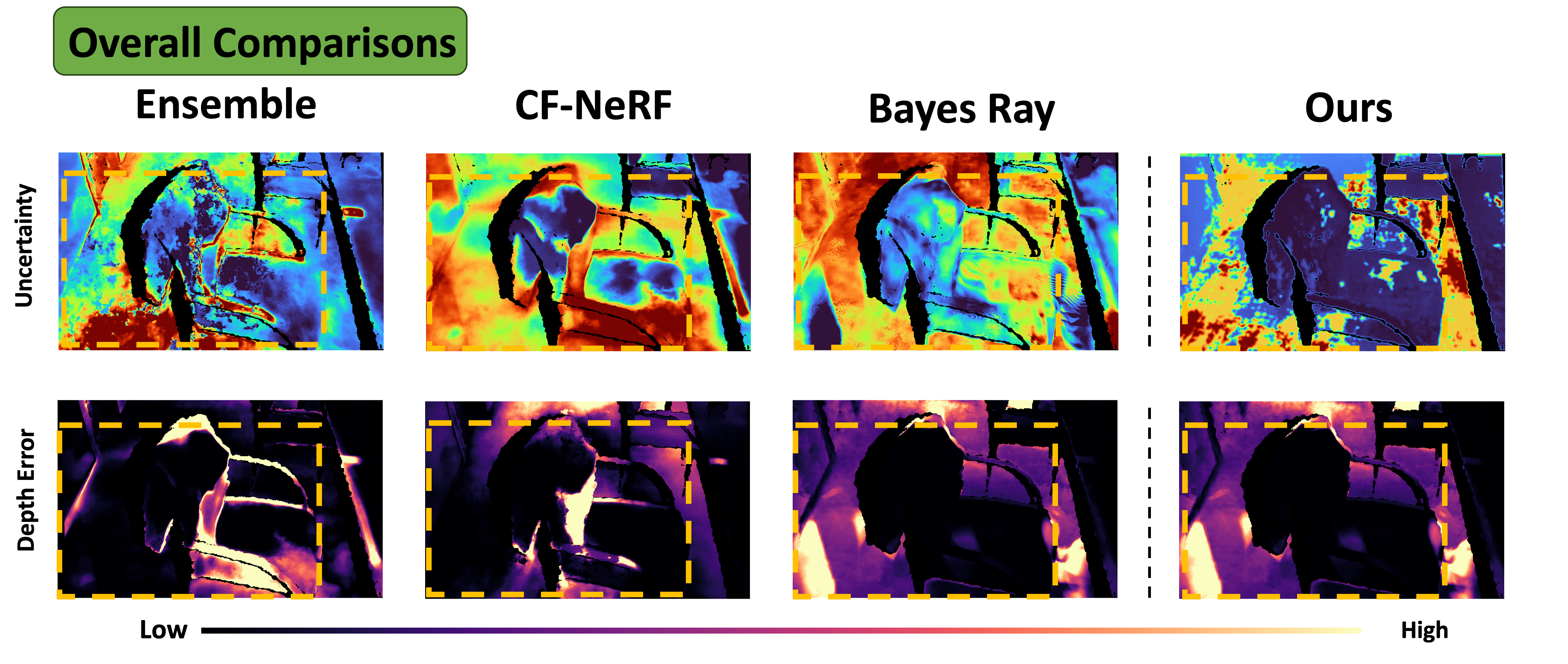
Uncertainty Modeling. The uncertainty and depth error maps are shown
with color bars specified. Uncertainty values and depth errors are normalized per test image for the result to be
comparable.
Application 2: Novel View Synthesis
ProvNeRF also helps with improving novel view synthesis by removing additional floaters.
Given a pretrained NeRF with floaters, we can query ProvNeRF on points along a training ray to obtain their provenance samples.
By matching the transmittance rendered from the provenance rays with that from the training ray, floaters in between can be removed. We formulate this as an additional regularizer on top of NeRF training.
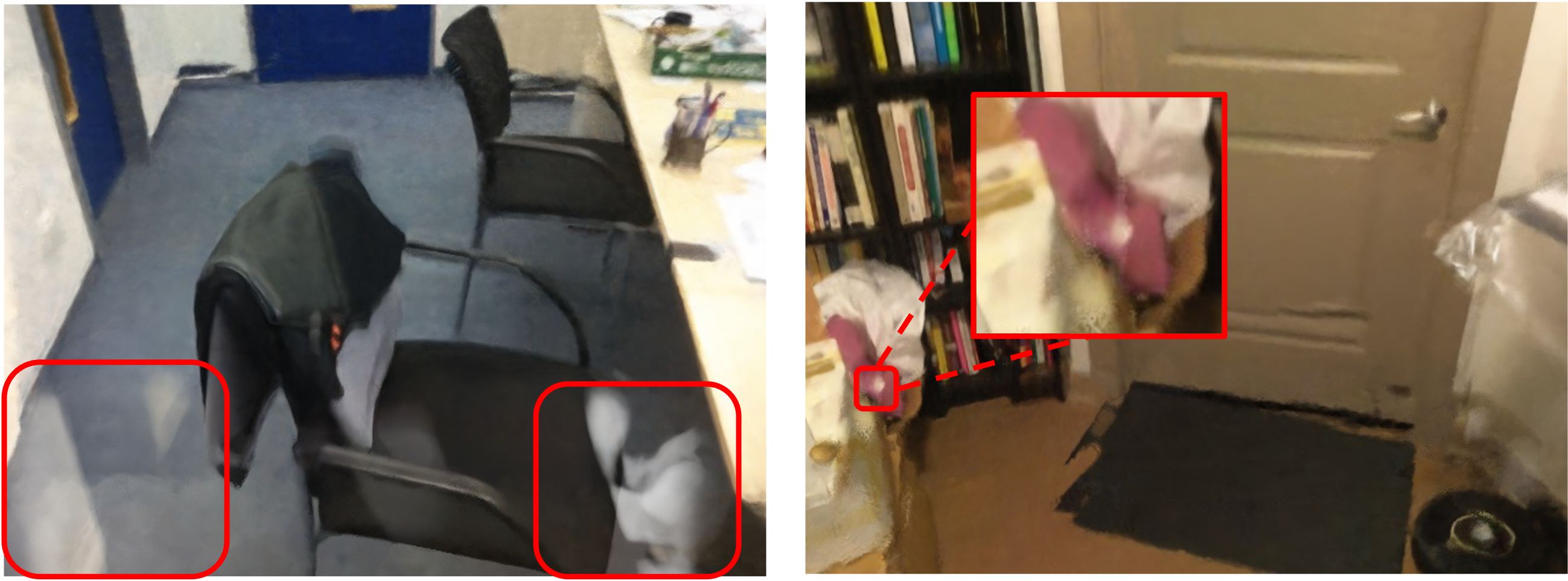


Notice we are able to remove clouds and small floaters from the original SCADE model.
Citation
@inproceedings{nakayama2024provnerf,
title={ProvNeRF: Modeling per Point Provenance in NeRFs as a Stochastic Field},
author={Kiyohiro Nakayama and Mikaela Angelina Uy and Yang You and Ke Li and Leonidas Guibas},
journal = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS)}},
year={2024}
}Acknowledgements
This work is supported by ARL grant W911NF-21-2-0104, a Vannevar Bush Faculty Fellowship, an Apple Scholars in AI/ML PhD Fellowship, a Snap Research Fellowship, the Outstanding Doctoral Graduates Development Scholarship of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.